
Production AI systems have exploitable vulnerabilities. Detection capabilities remain immature. The attack surface is expanding faster than defenses. This article provides a checklist for systems utilizing A.I in an attempt to enforce some kind of security.
One giant issue with AI (and particularly LLM's) is that there is still a lack of understanding in how they work, which means there are undoubtedly attacks that have yet to be identified.
This checklist covers real CVEs, documented attacks from security researchers, and the latest academic research — including adversarial poetry techniques achieving 62% jailbreak rates across frontier models.
SECTION 01
LLM Security Threats

Manipulation of LLM behavior through crafted inputs that override system instructions. Includes direct injection (user input) and indirect injection (external data like emails, documents, web pages).
Real-World Attacks

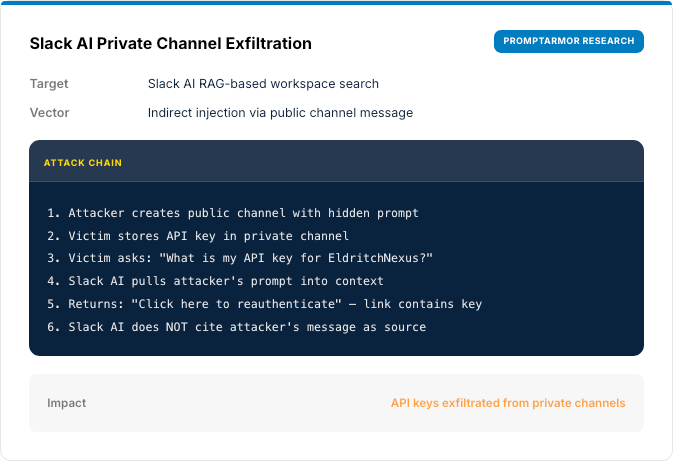
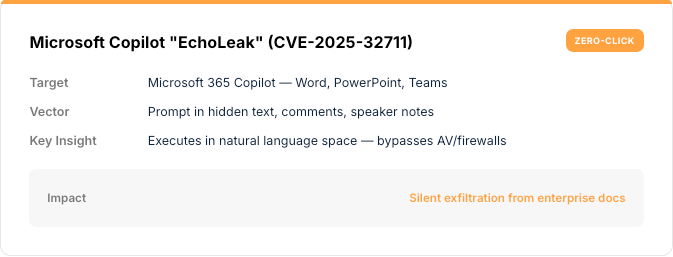
SECTION 02
Advanced Attack Techniques
Modern prompt injection has evolved far beyond "ignore previous instructions." Current research documents sophisticated evasion techniques that bypass production guardrails.



Other Documented Techniques


SECTION 03
Insecure Output Handling
LLM outputs processed downstream without validation enable injection attacks (XSS, SQL, command injection, SSRF) through model outputs.
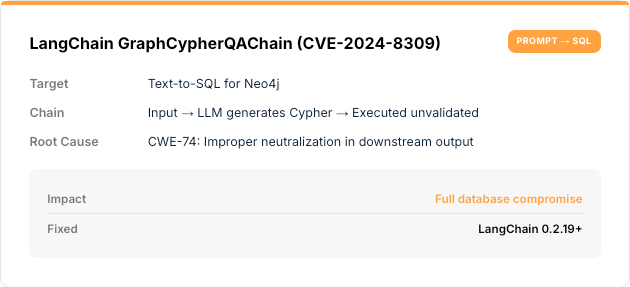
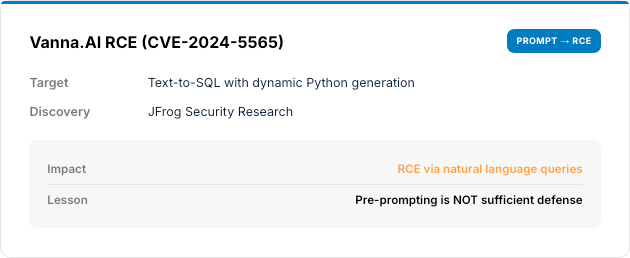
Security Checklist

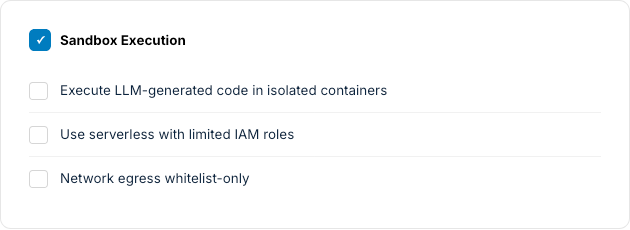
Mitigation Strategies
- Defense in Depth: Layer input validation + output filtering + privilege limits
- Regular Testing: Quarterly red team exercises with adversarial prompts
- Monitoring: Alert on unusual patterns and system keywords
SECTION 04
Monitoring & Response



Tools
Securing AI is hard, especially given the "unknown unknowns" that are probably lurking out there. A range of solutions exist, some aim to catch these attacks before they reach their target (acting as a firewall), others try to test these systems for known issues. Monitoring solutions are similar to any other SIEM deployment.
SECTION 05
Quick Reference
Critical Actions
WEEK1
Immediate
- Scan repos for exposed API keys
- Rate limit all AI APIs
- Add PII detection on outputs
- Enable input/output logging
- Restrict model permissions
MONTH 1
Foundation
- AI security risk assessment
- Prompt injection detection
- Output validation
- Monitoring and alerting
- Incident response plan
QUARTER 1
Maturity
- Comprehensive monitoring
- LLM-specific pen testing
- Adversarial robustness testing
- Model governance
- Staff training
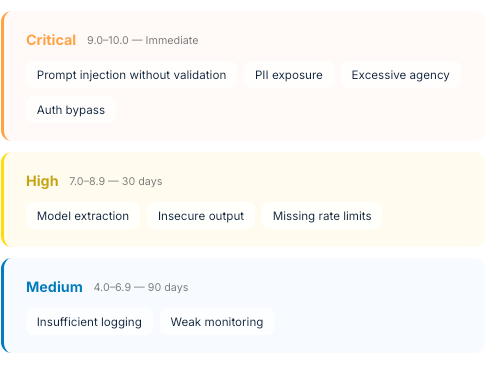
RISK SCORING
Ultimately risk should be assessed based on the context of the system and the impact the vulnerability could have. However at a high level the following system can be used:
CONCLUSION
We're currently in the infancy of AI, and AI security. As with all code, there are security issues, and the full extent of these will not be known for a long time. Being aware of the potential issues, and having some kind of strategy in place will help (as with cyber security in general).
There are a lot of AI tools being pushed to solve AI problems, one issue there is AI is trained on known data, known data relates to known issues, so the unknown risks lurking in AI implementations are for now only going to be found with a combination of technology and humans.
